Our research projects
SecureChange Mogentes Amber Diana Sensoria Decos Former projects
 |
Security Engineering for lifelong Evolvable Systems (SecureChange)
2009-2012 |
There is growing demand to continuously evolve systems to meet changing business
needs, new regulations and policies, novel technologies and computing infrastructures.
Unfortunately, the pace of required change affects our ability to ascertain and
maintain the quality of a system. Our objective is thus to develop techniques and
tools that ensure "lifelong" compliance to security, privacy and dependability
requirements for a long-running evolving software system. This is challenging because
these requirements are not necessarily preserved by system evolution.
The project will develop processes and tools that support design techniques for
evolution, testing, verification, re-configuration and local analysis of evolving
software. Our focus is on mobile devices and homes, which offer both great research
challenges and long-term business opportunities.
 |
Model-based Generation of Tests for Dependable Embedded Systems (MOGENTES)
2008-2010 |
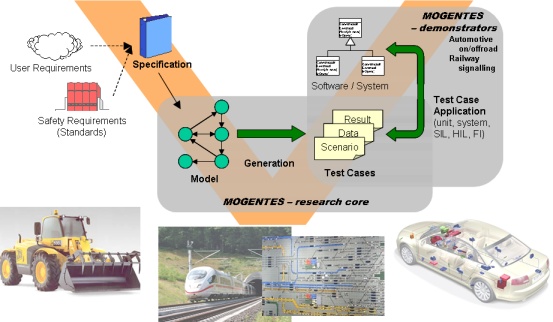
MOGENTES aims at significantly enhancing testing and verification of dependable embedded
systems by means of automated generation of test cases relying on development of new approaches
as well as innovative integration of state-of-the-art techniques. Driven by the needs of its
industrial partners, it will address both testing of non-functional issues like
reliability, e.g. by system stress and overload tests, and functional safety tests, meeting
the requirements of standards such as IEC 61508, ISO WD 26262, or AUTOSAR. MOGENTES will
demonstrate that different domains with a wide variety of requirements can significantly benefit
from a common model-based approach for achieving automated generation of efficient test cases
and for verifying system safety correctness using formal methods and fault injection, as this
approach increases system development productivity while achieving predictable system
dependability properties. For that purpose, proof-of-concept demonstrations will show the
applicability of the developed technologies in two application domains: railway and automotive.
In particular, MOGENTES aims at the application of these technologies in large industrial
systems, simultaneously enabling application domain experts (with rather little knowledge and
experience in usage of formal methods) to use them with minimal learning effort. All in all,
MOGENTES will increase knowledge and develop new techniques and tools in the area of verification
and validation of dependable embedded systems which can be applied in model-based development
processes also by non-experts in formal methods.
 |
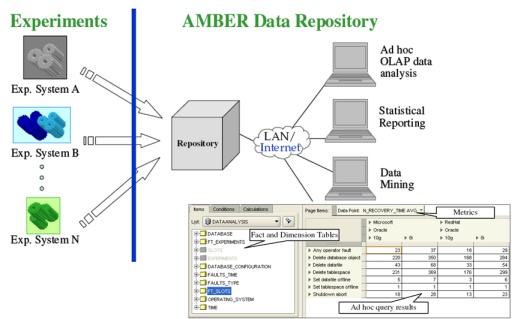
Assessing, Measuring and Benchmarking Resilience (AMBER)
2008-2009 |
AMBER is a FP7 Coordination Action. It will bring together leading research teams on
assessment, measurement, and benchmarking of resilience in computer systems in order to coordinate
the effort of defining metrics and benchmarks for comparative evaluation of the resilience of computer
systems and components. The consortium includes seven partners (universities of
Coimbra, Budapest, City, Chalmers, Florence, and Newcastle and the company ResilTech) from five
EU countries, which constitute core research groups on resilience assessment, and relies on a large
and representative Advisory Board that constitutes the necessary link between the coordination
action and the influential parties in industry and government, thus ensuring that the views of major
stake-holders are being taken into account by the AMBER Consortium.
AMBER aims to coordinate the study of resilience measuring and benchmarking in computer systems
and components, fostering European research in order to address the big challenges on resilience
assessment posed by current and forthcoming computer systems and computer-based infrastructures.
 |
Distributed, equipment Independent environment for Advanced avioNic Applications (DIANA)
2006-2009 |
The DIANA Project is the first step for the implementation of an enhanced avionics platform, named
AIDA (Architecture for Independent Distributed Avionics), providing secure distribution and execution
on virtual machines to avionics applications. Along with this objective, DIANA also aims at contributing
to the definition and standardization of the development and certification means needed to support this
novel platform.
The introduction of the DIANA concepts is expected to bring a significant development cost and time
reduction when compared to the situation where each aircraft electronic program has to develop a set
of specific hardware and software. The usage of very promising technologies, such as CORBA and JAVA
implementations in real time environment, and the update of standards will provide new opportunities
to create the future IME architectures for the next generation of aircraft.
 |
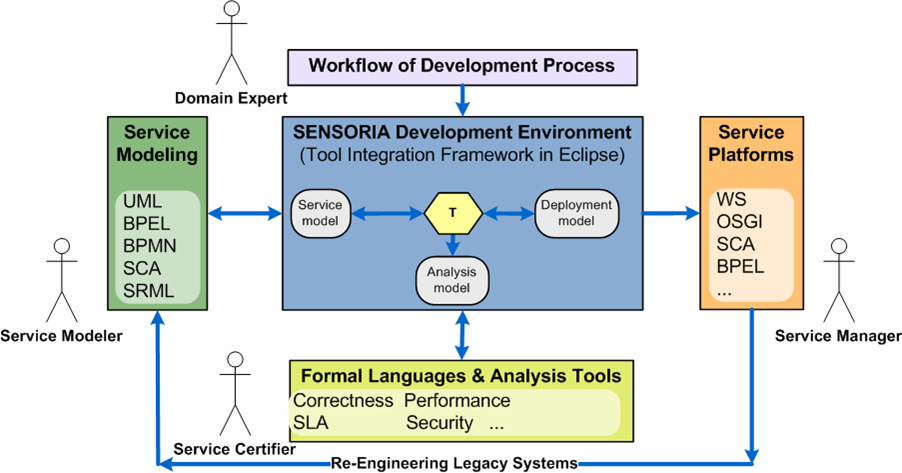
Software Engineering in Service-Oriented Overlay Computers (SENSORIA)
2006-2009 |
Service-oriented computing is an emerging paradigm where services are understood as
autonomous, platform-independent computational entities that can be described, published,
categorised, discovered, and dynamically assembled for developing massively distributed,
interoperable, evolvable systems and applications. These characteristics pushed service-oriented
computing towards nowadays widespread success, demonstrated by the fact that many large companies
invested a lot of efforts and resources to promote service delivery on a variety of computing
platforms, mostly through the Internet in the form of Web services. Tomorrow, there will be a
plethora of new services as required for e-government, e-business, and e-science, and other areas
within the rapidly evolving Information Society.
The aim of SENSORIA is to develop a novel comprehensive approach to the engineering of software
systems for service-oriented overlay computers where foundational theories, techniques and methods
are fully integrated in a pragmatic software engineering approach. It will focus on global services
that are context adaptive, personalisable, and may require hard and soft constraints on resources
and performance, and will take into account the fact that services have to be deployed on
different, possibly interoperating, global computers, to provide novel and reusable service-oriented
overlay computers.
 |
Dependable Embedded Components and Systems (DECOS)
2004-2007 |
 DECOS methodically targets, investigates, and develops approaches to significantly alleviate the
identified five key obstacles - Electronic Hardware Cost, Diagnosis and Maintenance, Dependability,
Development Cost, Intellectual Property (IP) Protection - to the deployment of advanced electronic functions
in embedded systems. The intent is to provide an integrated distributed execution platform and a set of
pre-validated hardware components and software modules and tools for the design of dependable embedded
systems. Generic design solutions for integrated dependable systems will be developed such that the invariance
of the design strategies and technology neutral interfaces are considered upfront as a design
objective. System design approaches that are applicable to diverse application domains will be
considered. DECOS targets automotive, aerospace, and control applications.
DECOS methodically targets, investigates, and develops approaches to significantly alleviate the
identified five key obstacles - Electronic Hardware Cost, Diagnosis and Maintenance, Dependability,
Development Cost, Intellectual Property (IP) Protection - to the deployment of advanced electronic functions
in embedded systems. The intent is to provide an integrated distributed execution platform and a set of
pre-validated hardware components and software modules and tools for the design of dependable embedded
systems. Generic design solutions for integrated dependable systems will be developed such that the invariance
of the design strategies and technology neutral interfaces are considered upfront as a design
objective. System design approaches that are applicable to diverse application domains will be
considered. DECOS targets automotive, aerospace, and control applications.
Former projects
- 2008-2009
GENeric Embedded SYStem Platform (GENESYS)
- 2006-2009
Highly Dependable Ip-based Networks and Services (HIDENETS)
Dependability and Security by Enhanced Reconfigurability (DESEREC) - 2006-2008
Safe Driver Machine Interface (DMI) for ERTMS automatic train control (SAFEDMI)
Resilience for Survivability in IST (RESIST) - 2005-2006
EU-conform, constructive safety assessment of railway control systems
- 2004-2007
Dependable Embedded Components and Systems (DECOS)
Quality of Service and Dependable Computer Networks - 2004-2006
Intelligent Measurement Data Processing for the Construction of Dependable IT Systems
- 2003-2006
Self-checking and run-time verification in computer programs
- 2002-2004
Operation Research Methods for the Analysis and Verification of Information Technology Systems
- 2001-2003
Integrated project management optimization
Development of robust object-oriented systems - 2000-2002
Framework for the development and testing of dependable and safety-critical systems
BPM based development of robust e-business applications
Dependability evaluation of object-oriented systems - 2000-2001
UML based modelling and design of technological processes
- 1999-2001
Object-oriented modelling and optimization of industrial processes
Formal verification of safety requirements in fault tolerant systems
Automated verification and validation of UML-based models of information systems
Constructive quality assurance of information services - 1998
Object-oriented fine programming of industrial production processes
High-level integrated design environment for dependability - 1997-1999
Reconfigurable elements in the design and validation of multiprocessors
Knowledge management and transfer in the information society - 1997
Functional test generation and diagnosis
- 1996
Formal methods in information science